Logic Gates
Inverter (NOT Gate)

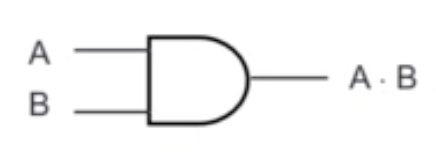
AND Gate
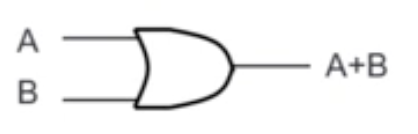
OR Gate
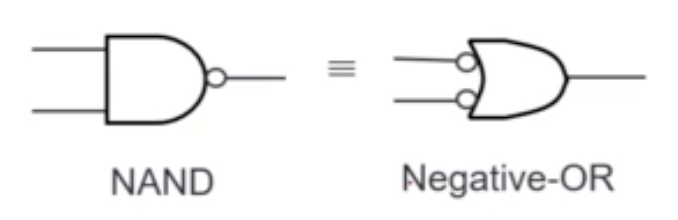
NAND Gate

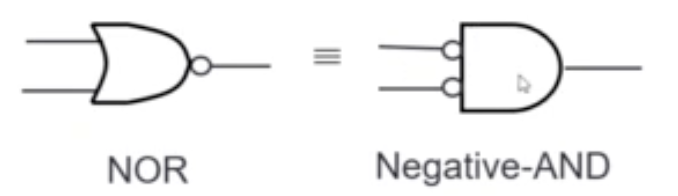
NOR Gate

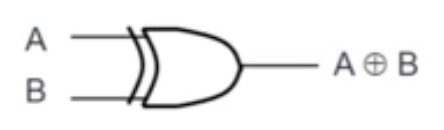
XOR Gate
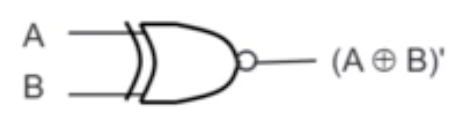
XNOR Gate
Logic Circuits
- Contain logic gates
Fan-in:the number of inputs of a gate.- Gates may have fan-in more than 2
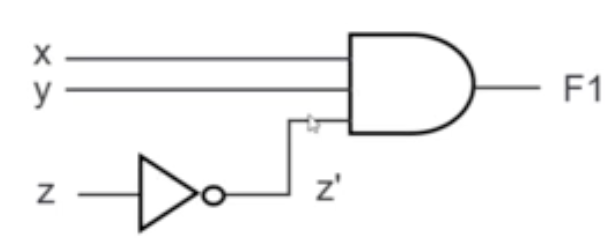
Given a boolean expression, we may implement it as a logic circuit. e.g.
Universal Gates
AND/OR/NOT gates are sufficient for building any Boolean function.
- They are known as a complete set of logic
- Other gates are used for:
- Usefulness (e.g. XOR gate for parity bit generation)
- Economical
- Self-sufficient (eg: NAND/ NOR gates)
NAND Gate
- is also a complete set of logic
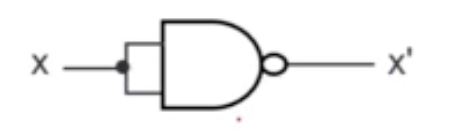
- Proof by building NOT/AND/OR using only NAND gates
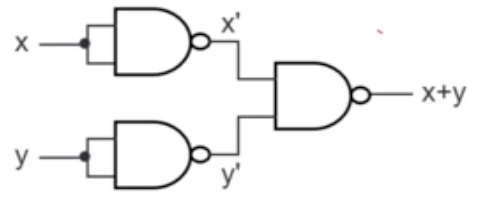
- → NOT operation achieved!
- → AND operation achieved!
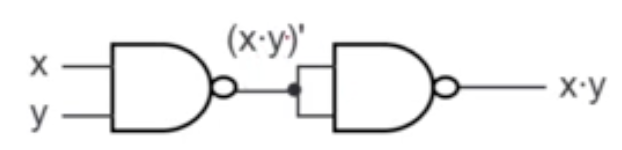
- → OR operation achieved!
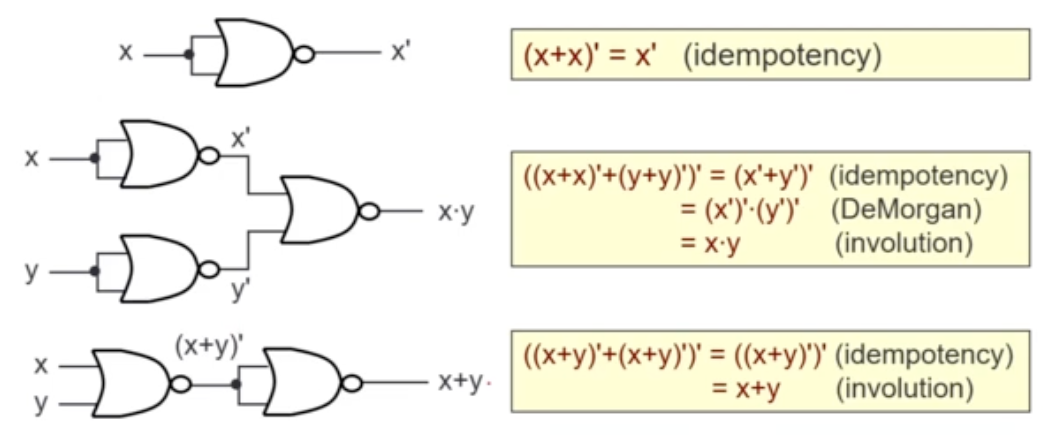
NOR Gate
- is also a complete set of logic!
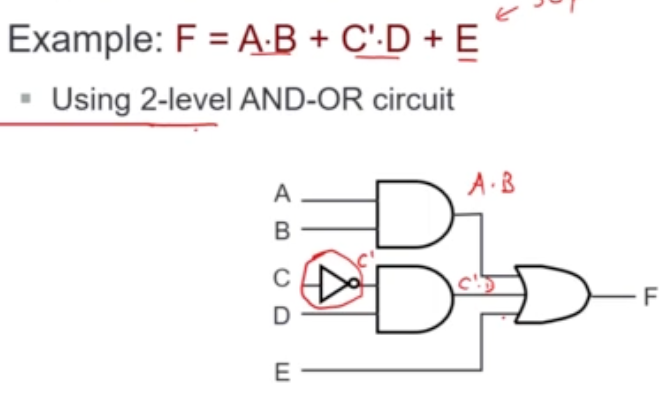
SOP and NAND Circuits
- An SOP expression can be easily implemented using
- 2-level AND-OR circuit
- 2-level NAND circuit
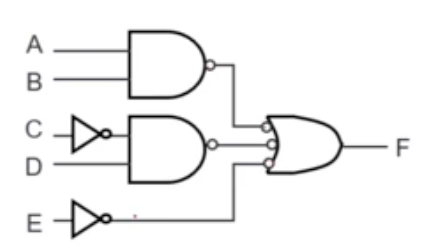
POS and NOR Circuits
- likewise, a POS expression can be easily implemented using
- e.g.
- 2-level OR-AND circuit
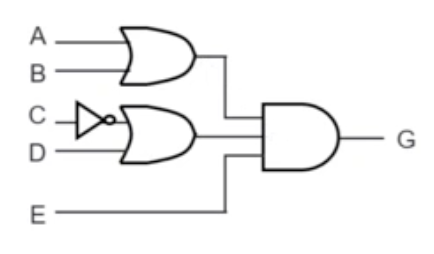
- 2-level NOR circuit
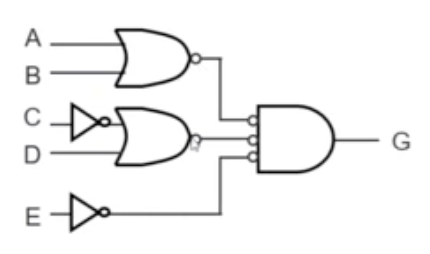
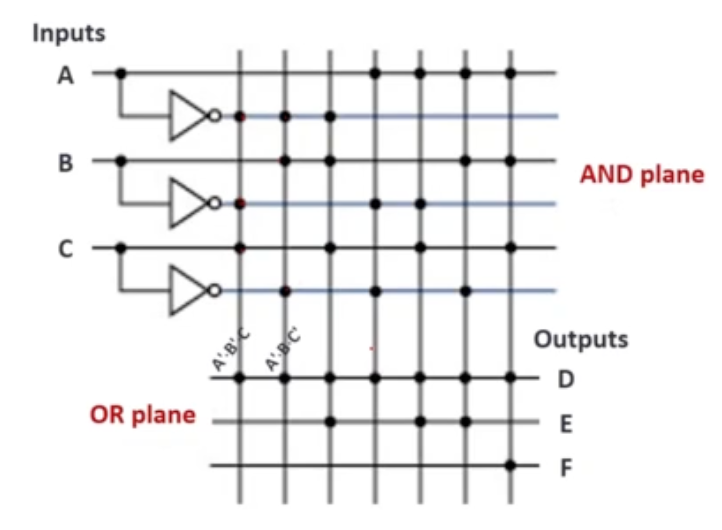
Programming Logic Array (PLA)
A programmable integrated circuit
- implements sum-of-product circuits (allow multiple outputs)
2 Stages
- AND gates = product terms
- OR gates = outputs
Example
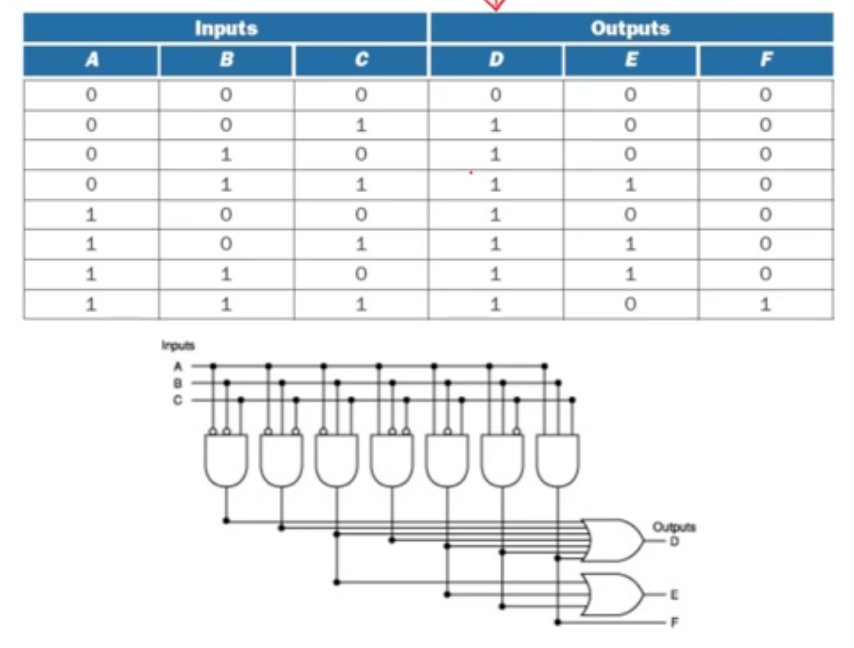
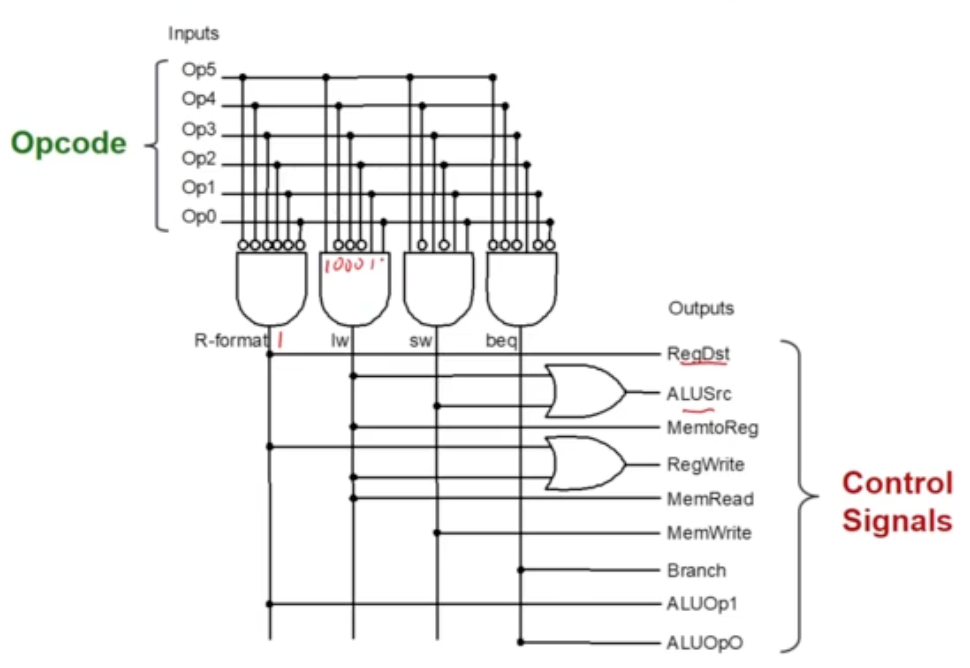
Example: Combinational Circuit implementation in MIPS
Read only Memory (ROM)
- Similar to PLA
- Set of input (called addresses)
- set of outputs
- programmable mapping between inputs and outputs
- Fully decoded: able to implement any mapping
- In contrast, PLAs may not be able to implement a given mapping due to not having enough minterms.